IntelliMIND - Methylation
- Test Requisition Form
- Methylation Chart
- Sample Report
- Brochure
- Blood Collection Video
IntelliMIND - Methylation
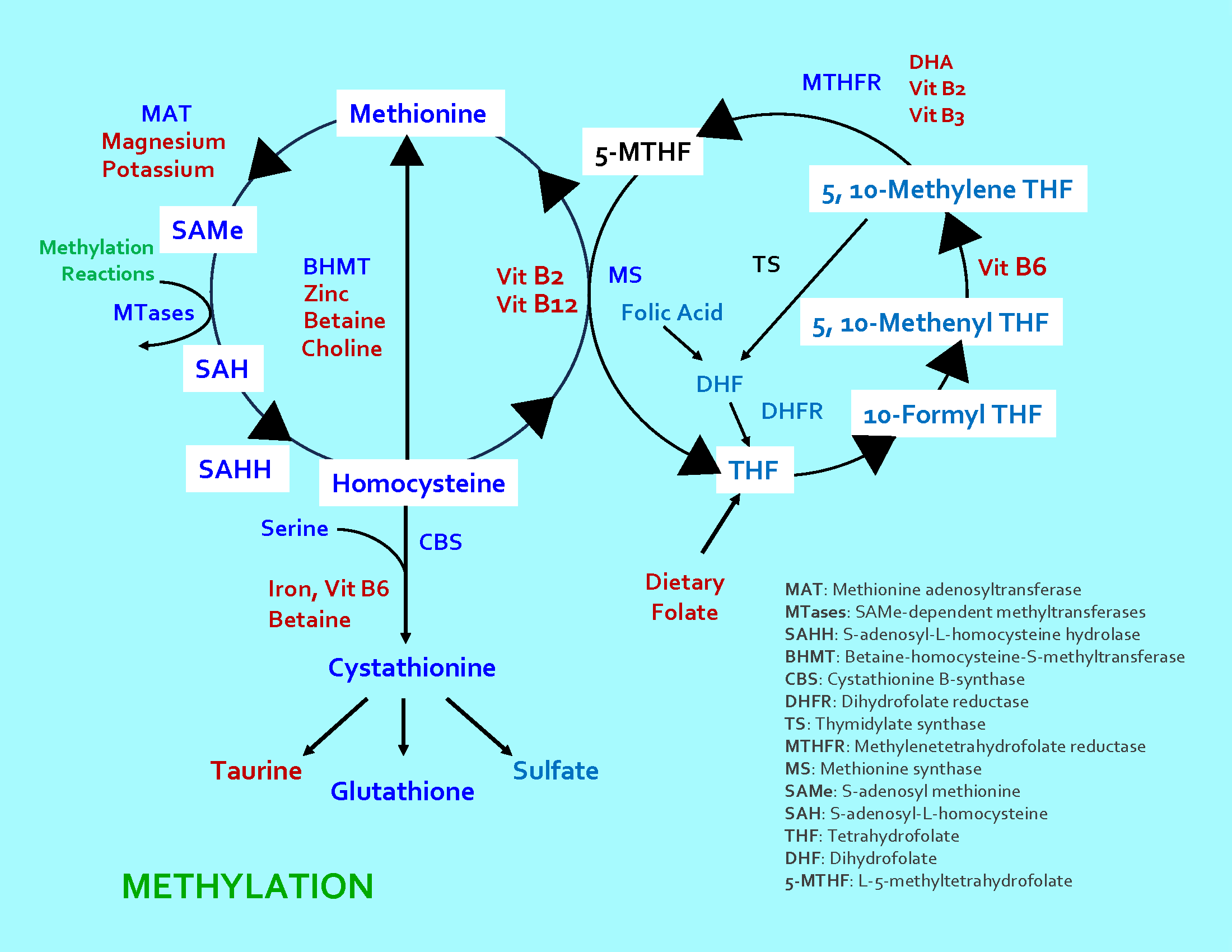
Methylation is a fundamental biochemical process where a methyl group (CH3) is transferred and attached to another molecule, typically a larger one. Methylation, particularly in the context of DNA, refers to the addition of a methyl group (CH3) to the DNA molecule, which can influence gene expression. Various genes and proteins facilitate or are influenced by methylation.
DNA Methylation is a primary epigenetic mechanism. While genetics refers to the actual DNA sequence (the genes), epigenetics refers to external modifications to DNA that turn genes “on” or “off.” These modifications do not change the DNA sequence but affect how genes are expressed. Epigenetic changes, such as DNA methylation, are inheritable and play crucial roles in development, aging, and even memory formation.
The MTHFR gene encodes the enzyme methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase, which plays a vital role in converting folic acid (vitamin B9) into its active form, 5-methyltetrahydrofolate. This active form of folate is essential in the methylation cycle, a critical biochemical pathway in the body. Mutations or variants in the MTHFR gene can lead to reduced activity of the enzyme.
MTHFR Variants:
C677T (c.665C>T): This variant can lead to a significant reduction in MTHFR enzyme activity, especially if an individual carries two copies of the T allele (homozygous). It has been associated with elevated homocysteine levels, cardiovascular diseases, and other health issues.
A1298C (c.1286A>C): This variant is typically considered less severe than the C677T variant but can still affect enzyme function, especially if present in combination with other variants.
The MTRR (5-Methyltetrahydrofolate-Homocysteine Methyltransferase Reductase) gene encodes an enzyme that is part of the folate metabolism pathway, ensuring the conversion of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF) to tetrahydrofolate (THF), which is an essential step in the methionine cycle and homocysteine metabolism.
The COMT (Catechol-O-Methyltransferase) gene encodes an enzyme that plays a role in the breakdown of catecholamines, which are neurotransmitters such as dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine. Variations in the COMT gene have been associated with differences in enzyme activity and neurotransmitter metabolism, affecting neurotransmitter levels in the brain.
The implications of these variants can vary widely among individuals and may include:
Elevated Homocysteine Levels: Reduced MTHFR activity can lead to increased levels of homocysteine in the blood, a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases and other health problems.
Neurological and Mental Health Issues: Some studies have suggested a link between MTHFR variants and neurological conditions, depression, anxiety, and cognitive impairment.
Pregnancy Complications: MTHFR variants have been explored for potential associations with pregnancy-related complications such as recurrent miscarriages and neural tube defects.
Complex Interactions: The effects of MTHFR variants can be influenced by diet, lifestyle, other genetic factors, and overall health. For example, adequate intake of folate-rich foods or supplements can often mitigate potential negative effects.
IntelliMIND Methylation MTHFR Gene Variants DNA Test
Price: $99.00
IntelliMIND Methylation MTHFR, MTRR, COMT Gene Variants DNA Test
Price: $149.00
IntelliMIND Methylation Blood Test
Blood Test: 12 Analytes tested: Homocysteine, Iron, Magnesium, Potassium, Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin), Vitamin B3 (Niacin), Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine), Vitamin B9 (Folate), Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin), Methyl B12, Vitamin D 25-OH, Zinc
Price: $249.00
MTHFR (methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase) Gene Variants
MTHFR (methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase) gene variants can indeed have an impact on cognitive function, although the relationship is complex and not fully understood. The MTHFR enzyme is involved in the conversion of folate into its active form, which is crucial in a biochemical process called the methylation cycle.
Here’s how MTHFR variants relate to cognitive function:
- Homocysteine Levels: The MTHFR enzyme plays a key role in converting homocysteine into methionine. Certain variants of the MTHFR gene, such as the c.665C>T (C677T) and c.1286A>C (A1298C), can reduce the enzyme’s activity, leading to increased levels of homocysteine in the blood. Elevated homocysteine has been linked to various health problems, including cardiovascular diseases and cognitive decline.
- Folate Metabolism: Reduced MTHFR activity due to gene variants can also disrupt folate metabolism. Since folate is essential for DNA synthesis and repair, as well as neurotransmitter synthesis, disruptions in folate metabolism might have implications for cognitive function.
- Impact on Cognitive Function and Neurological Health: Some studies have suggested that MTHFR variants may be associated with an increased risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, cognitive impairment, depression, and other mental health disorders. The mechanisms are not entirely clear, but they likely involve disruptions in methylation processes and increased oxidative stress.
- Consideration of Other Factors: It’s crucial to note that the relationship between MTHFR variants and cognitive function is not straightforward and can be influenced by various dietary, lifestyle, genetic, and environmental factors. For example, adequate intake of folate and other B-vitamins can often mitigate the potential negative effects of MTHFR variants on homocysteine levels and cognitive function.
- Therapeutic Approaches: For individuals with MTHFR variants who show elevated homocysteine levels or other related issues, healthcare providers might recommend dietary adjustments, supplementation with specific forms of folate (such as 5-methyltetrahydrofolate), or other personalized interventions.
- Need for Personalized Interpretation: Because the impact of MTHFR variants on cognitive function can vary widely among individuals, it is generally best to interpret these genetic findings in the context of a comprehensive health assessment. Healthcare providers with expertise in this area can provide individualized guidance and recommendations.
Test Details
The MTHFR C677T (c.665C>T) variant is a specific single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the MTHFR gene, which encodes the enzyme methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. This enzyme plays a critical role in the conversion of folic acid into its biologically active form, 5-methyltetrahydrofolate, a process that’s vital for several biochemical reactions, including the conversion of homocysteine to methionine.
Here’s a more detailed look at this particular variant:
Genotypes and Enzyme Activity:
- CC (c.665C>C): Homozygous for the normal allele, with typical MTHFR enzyme activity.
- CT (c.665C>T): Heterozygous, with one normal allele and one variant allele, leading to moderately reduced enzyme activity.
- TT (c.665T>T): Homozygous for the variant allele, leading to significantly reduced enzyme activity.
Potential Health Implications:
- Elevated Homocysteine Levels: Reduced activity of the MTHFR enzyme can lead to higher levels of homocysteine in the blood, a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases.
- Neurological and Cognitive Impact: Some studies have suggested a link between the C677T variant and neurological conditions, cognitive impairment, and mental health disorders like depression and anxiety.
- Pregnancy Complications: The variant has been explored for potential associations with pregnancy-related complications, such as neural tube defects.
- Interactions with Diet and Lifestyle: The effects of the C677T variant can be influenced by dietary folate intake, other nutritional factors, and overall health. Adequate intake of folate may help mitigate potential negative effects.
Testing and Management:
- Genetic Testing: Testing for the C677T variant can be done through a blood or buccal/saliva sample, usually in conjunction with a broader health assessment.
- Management and Intervention: Individuals with the variant, especially those who are homozygous (TT), may benefit from personalized dietary guidance and possibly supplementation with specific forms of folate, such as 5-methyltetrahydrofolate.
Complexities and Considerations:
- The relationship between the C677T variant and health is complex and multifactorial. Not everyone with the variant will experience health problems.
- It’s often best to interpret the presence of the C677T variant in the context of overall health, lifestyle, and other genetic factors.
- Guidance from healthcare providers, genetic counselors, or other professionals with expertise in genetics and nutrition is essential for personalized interpretation and recommendations.
In summary, the MTHFR C677T variant can affect enzyme function and has potential implications for various aspects of health. However, the relationship is complex, and individualized assessment and guidance are key to understanding and managing the potential effects of this variant.
The MTHFR variant A1298C (c.1286A>C) is another common single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the MTHFR gene, which encodes the enzyme methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. This enzyme is crucial in converting folic acid into its active form, 5-methyltetrahydrofolate, essential for many biochemical reactions in the body.
Here’s a more detailed exploration of the A1298C variant:
Genotypes and Enzyme Activity:
- AA (c.1286A>A): Homozygous for the normal allele, with typical MTHFR enzyme activity.
- AC (c.1286A>C): Heterozygous, carrying one normal allele and one variant allele, leading to moderately reduced enzyme activity.
- CC (c.1286C>C): Homozygous for the variant allele, which may further reduce enzyme activity.
Potential Health Implications:
- Moderate Impact on Enzyme Function: The A1298C variant generally has a milder impact on enzyme function compared to the C677T variant, but it can still influence folate metabolism.
- Homocysteine Levels: While the relationship is not as strong as with the C677T variant, some studies suggest that the A1298C variant might contribute to elevated homocysteine levels, particularly if other risk factors are present.
- Potential Link to Health Conditions: Some research has explored possible associations between the A1298C variant and various health conditions, such as depression, migraines, and recurrent miscarriages, although the evidence is mixed and complex.
- Interactions with Other Variants: The A1298C variant can interact with other MTHFR variants (such as C677T) and other genetic factors, leading to a more complex picture of enzyme function and potential health implications.
Testing and Management:
- Genetic Testing: Testing for the A1298C variant can be done through a blood or buccal/saliva sample, typically in conjunction with an overall health assessment.
- Management and Intervention: Individuals with the A1298C variant may benefit from personalized dietary guidance, including ensuring adequate folate intake. Supplementing with the active form of folate (5-methyltetrahydrofolate) might be recommended in some cases.
Complexities and Considerations:
- The relationship between the A1298C variant and health is multifaceted, and not everyone with the variant will experience health issues.
- The presence of the A1298C variant should be interpreted in the context of overall health, diet, lifestyle, and other genetic factors.
- Consulting with healthcare providers or genetic counselors with expertise in this area is important for personalized interpretation and recommendations.
In summary, the MTHFR A1298C variant can have implications for enzyme function and potentially impact various aspects of health. The relationship is complex, and a thorough assessment, including consideration of other genetic, dietary, and lifestyle factors, is essential for understanding and managing the potential effects of this variant.
- Buccal Swab or Saliva Swab
7 – 10 days
Price: $99.00

