Kidney Function Test
$89.00
A kidney function test, also known as a renal panel or kidney function test, is used to assess the health and function of the kidneys. It involves measuring various markers in the blood that provide information about kidney function, electrolyte balance, and waste product clearance.
Analytes in this test: 12 Total Analytes:- Albumin, Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN), Creatinine, BUN/Creatinine, EGFR, Glucose, Sodium, Potassium, Phosphorus, Calcium, Chloride, Urinalysis.
Description
About the Test
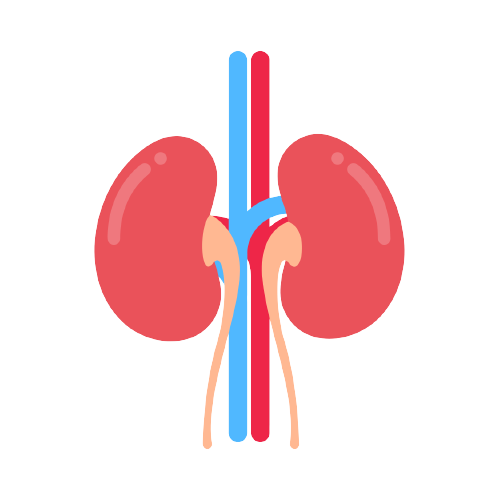
Kidney health refers to the overall well-being and proper functioning of the kidneys. The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs located in the lower back that filter waste products from the blood, regulate the balance of fluids and minerals in the body, and produce hormones that regulate blood pressure, promote red blood cell production, and support bone health.
If you have a family history of kidney disease, are at risk for developing kidney disease due to other health conditions, or have any symptoms such as pain in the lower back, swelling in the legs or feet, frequent urination, or changes in the amount or appearance of urine, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional. Early detection and treatment can help slow the progression of kidney disease and prevent complications.